Molecular Beam Epitaxy |
|
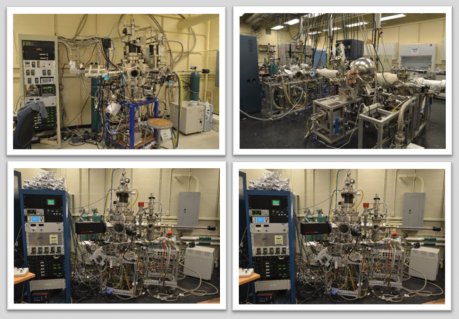 |
Materials synthesis capabilities consist of five molecular beam epitaxy systems in four laboratories. One system is currently dedicated to developing ferroelectric monolayers and growing oxides on semiconductors. The other three systems are each research grade MBE systems. These systems consist of a loadlock and MBE chamber with thermal sources, RF plasma oxygen sources, and/or electron beam sources. One of them is used as a teaching tool for undergraduates and features custom automation and interlocks. The MBE systems focus on the deposition of nickelates, titanates, manganites, selenides, and tellurides on up to 50 mm-diameter substrates. A fifth MBE system is located on the experimental floor of the National Synchrotron Light Source II (NSLS II) and can transfer and grow films remotely. |
Rotating Anode X-Ray Source |
|

|
The Rigaku rotating anode x-ray diffractometer (XRD) is now a workhorse for characterizing epitaxial thin films. The combination of large x-ray flux from a rotating anode and new, efficient x-ray optics make this diffractometer tool ideal for characterizing oxide thin films with thicknesses as small as a few nanometers…more |
Cryogen-free Physical Property Measurement System (PPMS - Dynacool) |
|

|
The closed-cycle, cryogen-free Physical Property Measurement System (PPMS - Dynacool) enables low temperature and high magnetic field transport measurements without the need for liquid helium. The system is capable of measuring bulk and thin film samples in a temperature range of 1.8 to 400K up to fields of 9T and comes equipped with both DC and AC measurement capabilities. The cryogen-free temperature control eliminates the overhead associated with refilling the system, allows for continuous operation for indefinite periods of time, and leads to faster magnetic field control. This instrument is already being used by multiple groups to study a variety of materials including oxide thin films and semiconductor nanomaterials |
Quantum Design MPMS Squid Magnetometer |
|
 |
The SQUID detects and measures magnetic moments, allowing the magnetization and magnetic susceptibility to be determined. Applications of the SQUID magnetometer include measurements of small quantities of paramagnetic ions, characterization of magnetic materials, and quantitative determination of the number of unpaired electrons in samples. The MPMS-XL provides solutions for a unique class of sensitive magnetic measurements in key areas such as high-temperature superconductivity, biochemistry, and magnetism. Fundamentals of Magnetism for MPMS provides an introduction to the background physics and the MPMS, and may be helpful to a beginning user. |
|
|
|